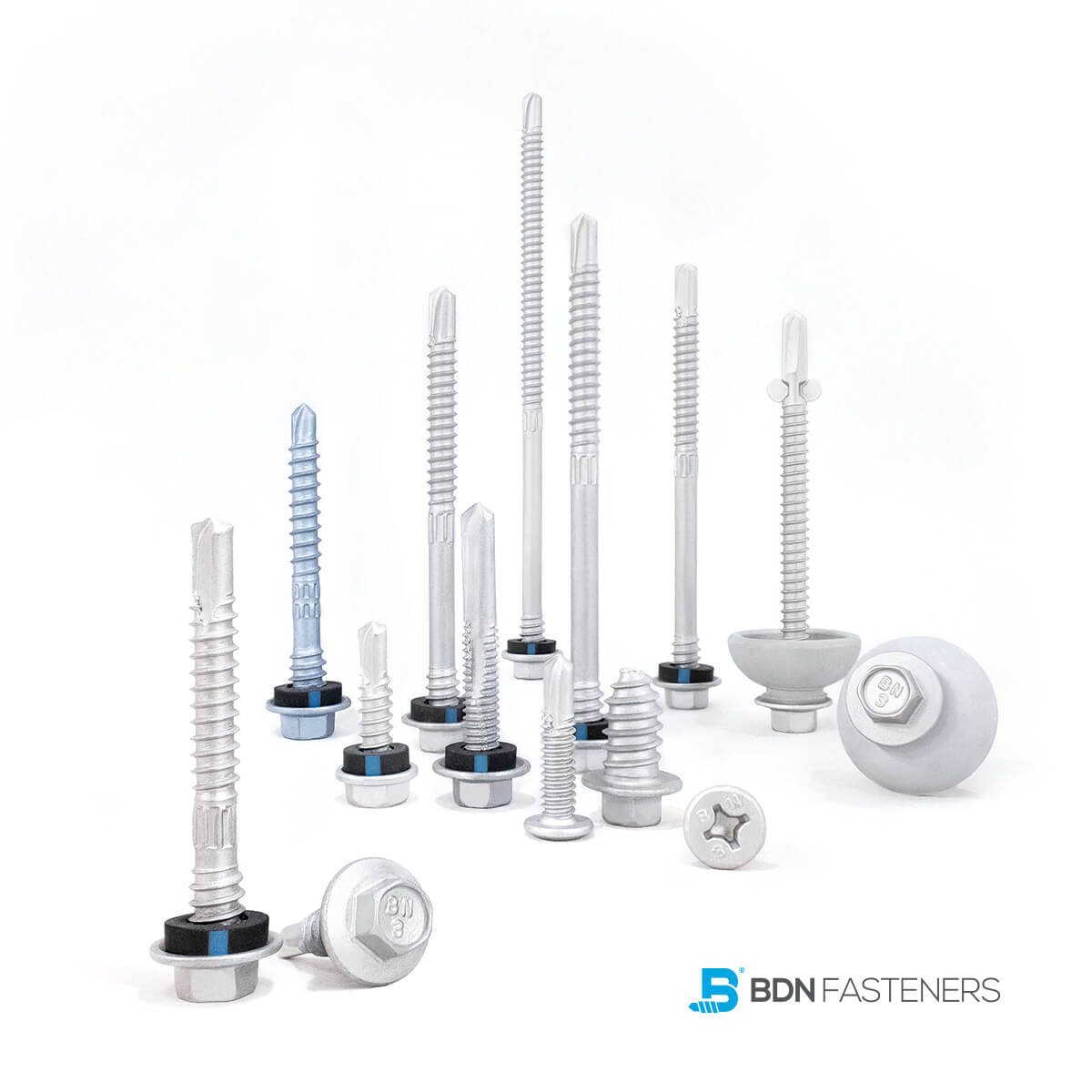
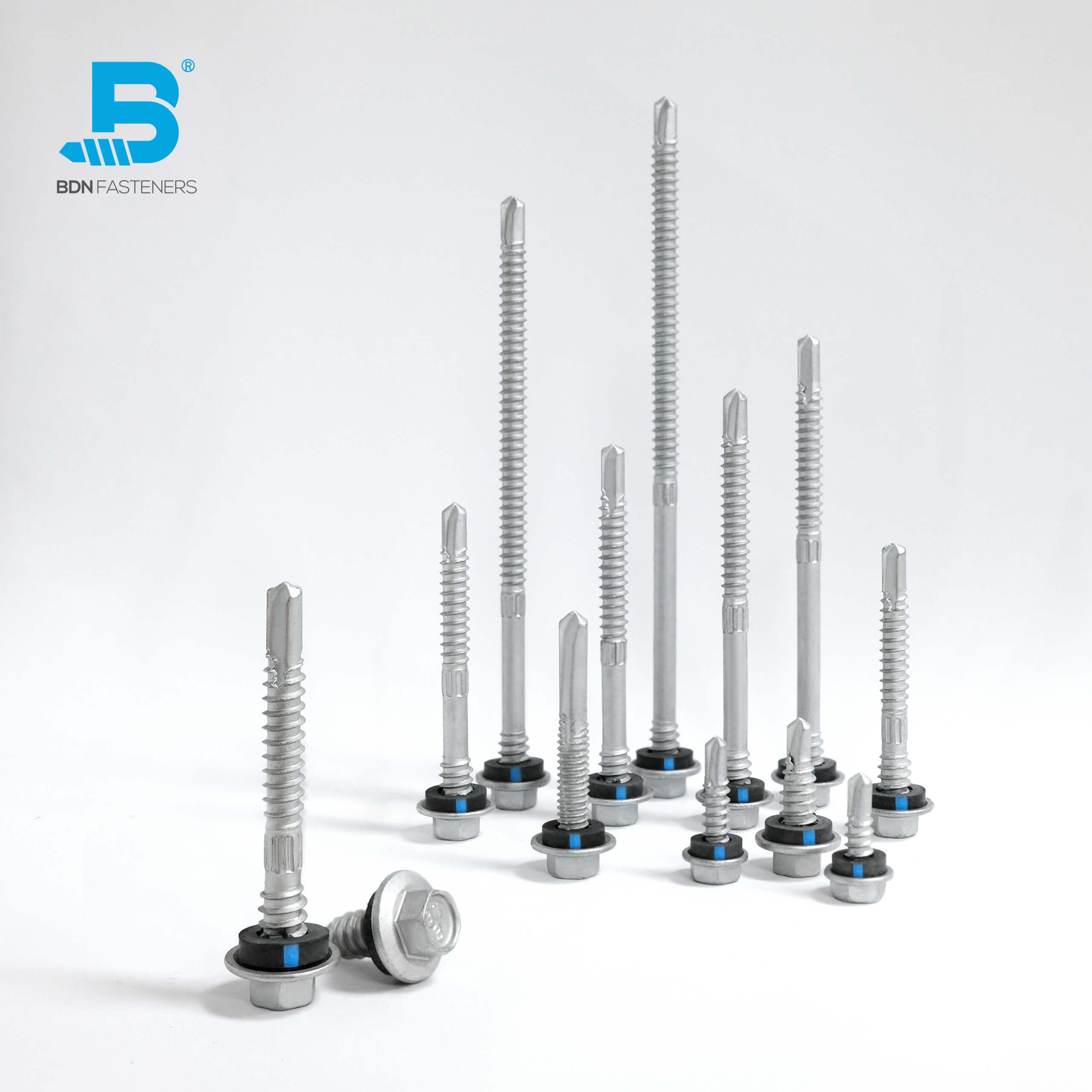
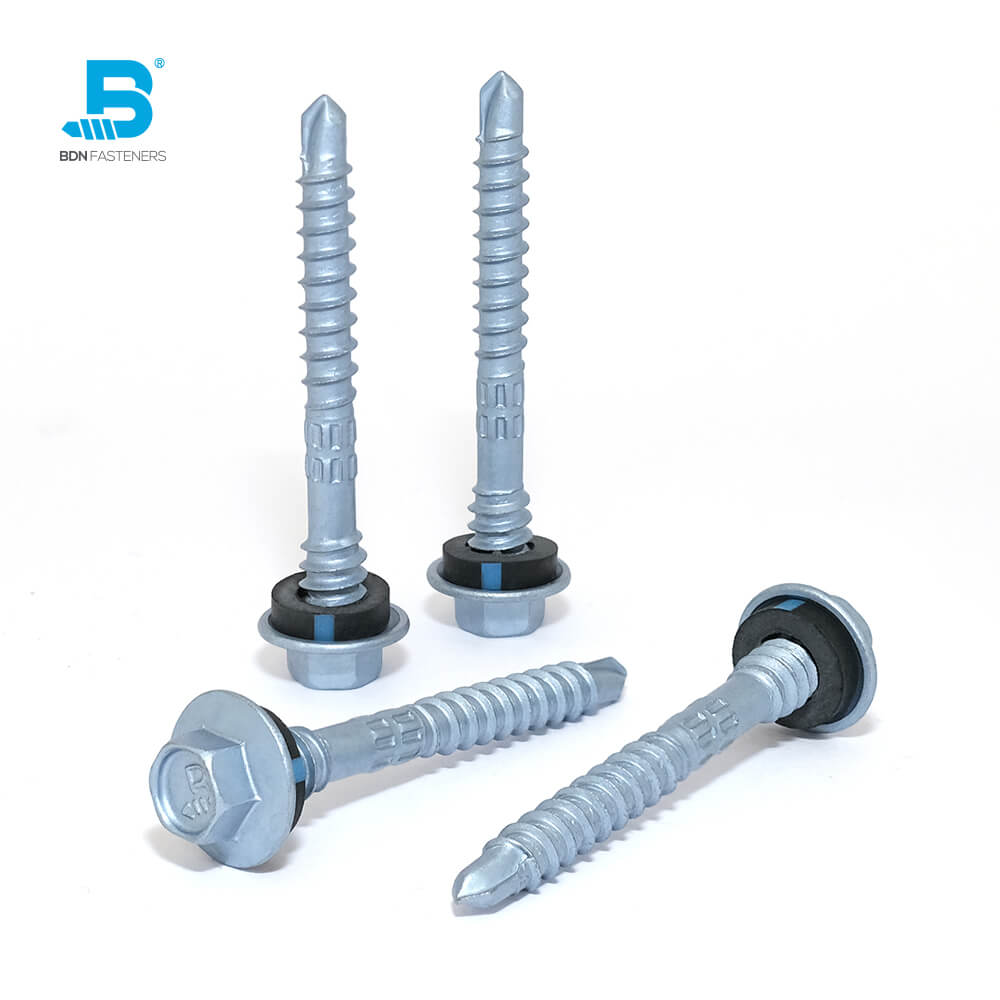
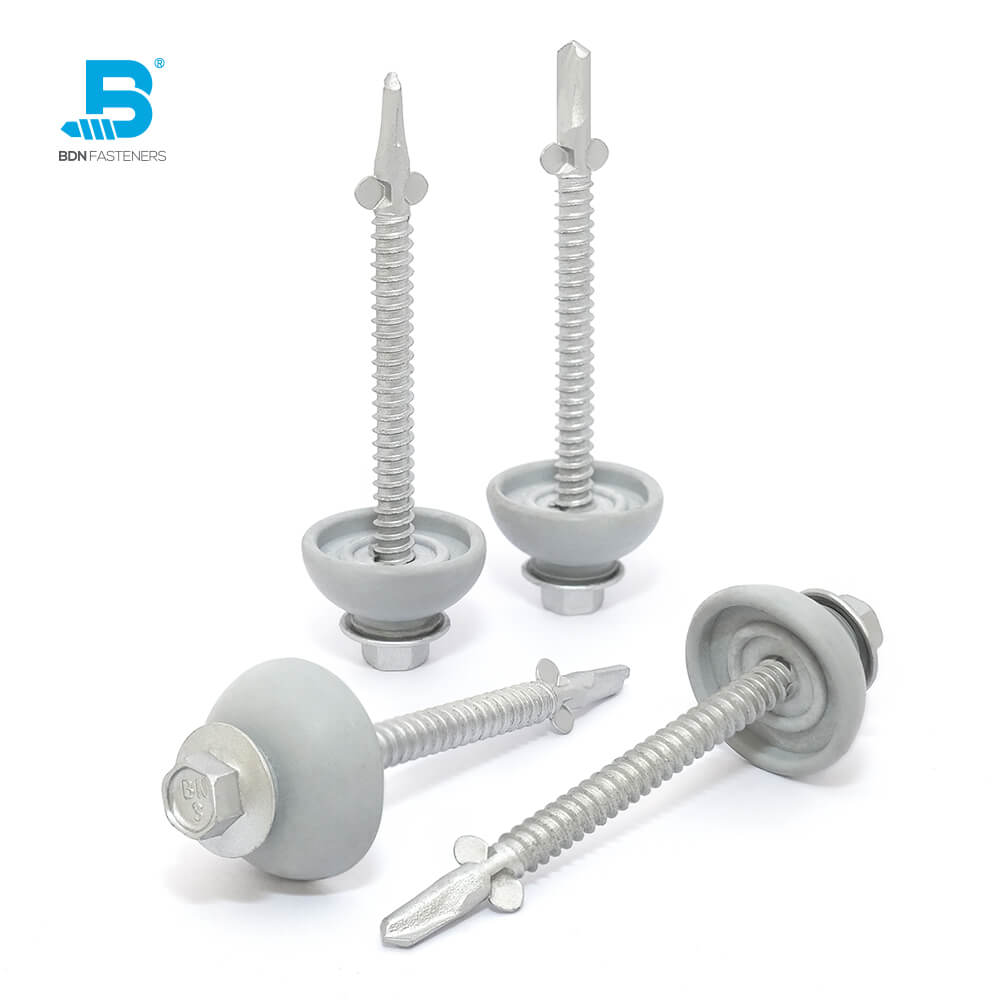
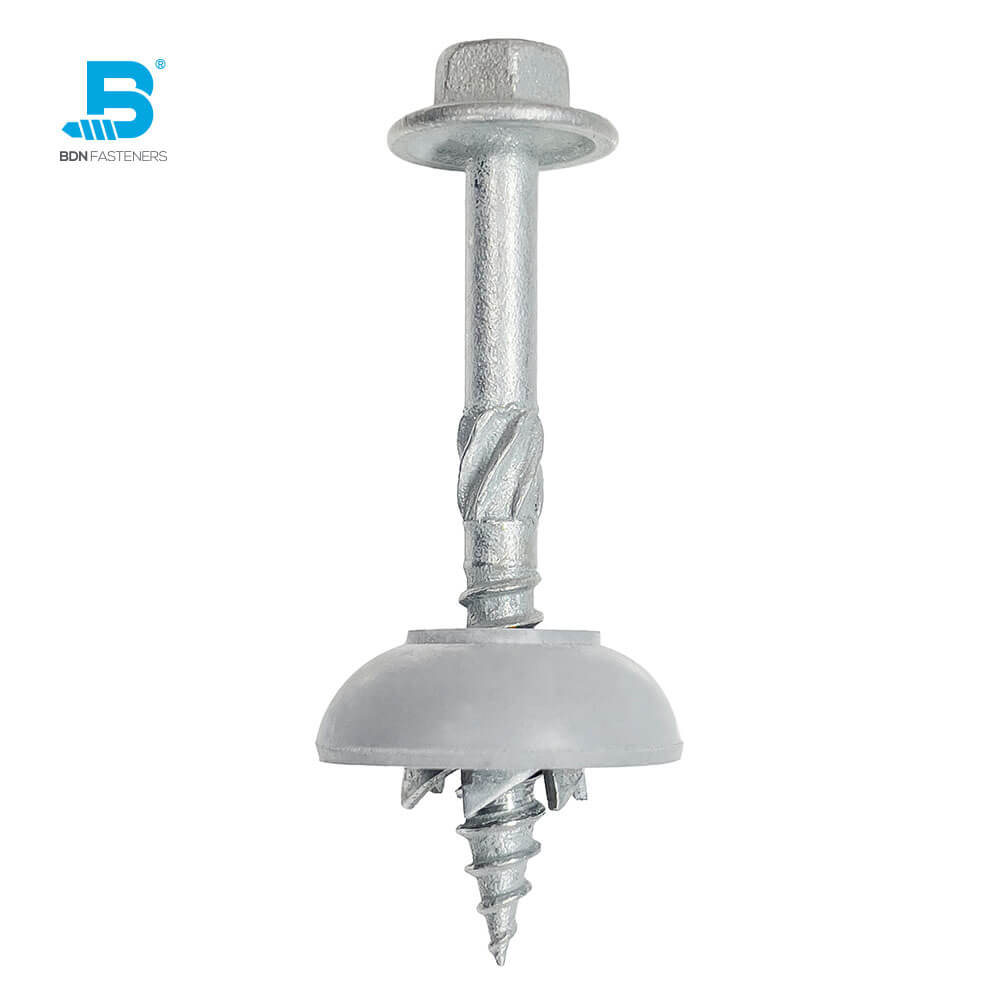
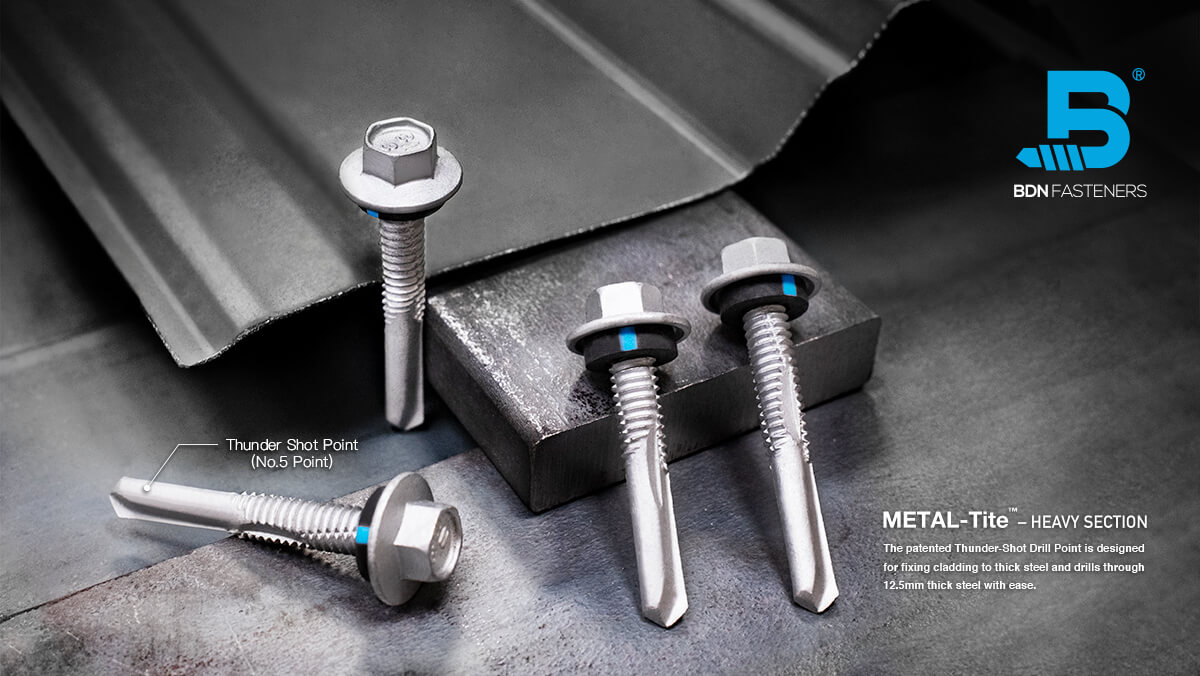
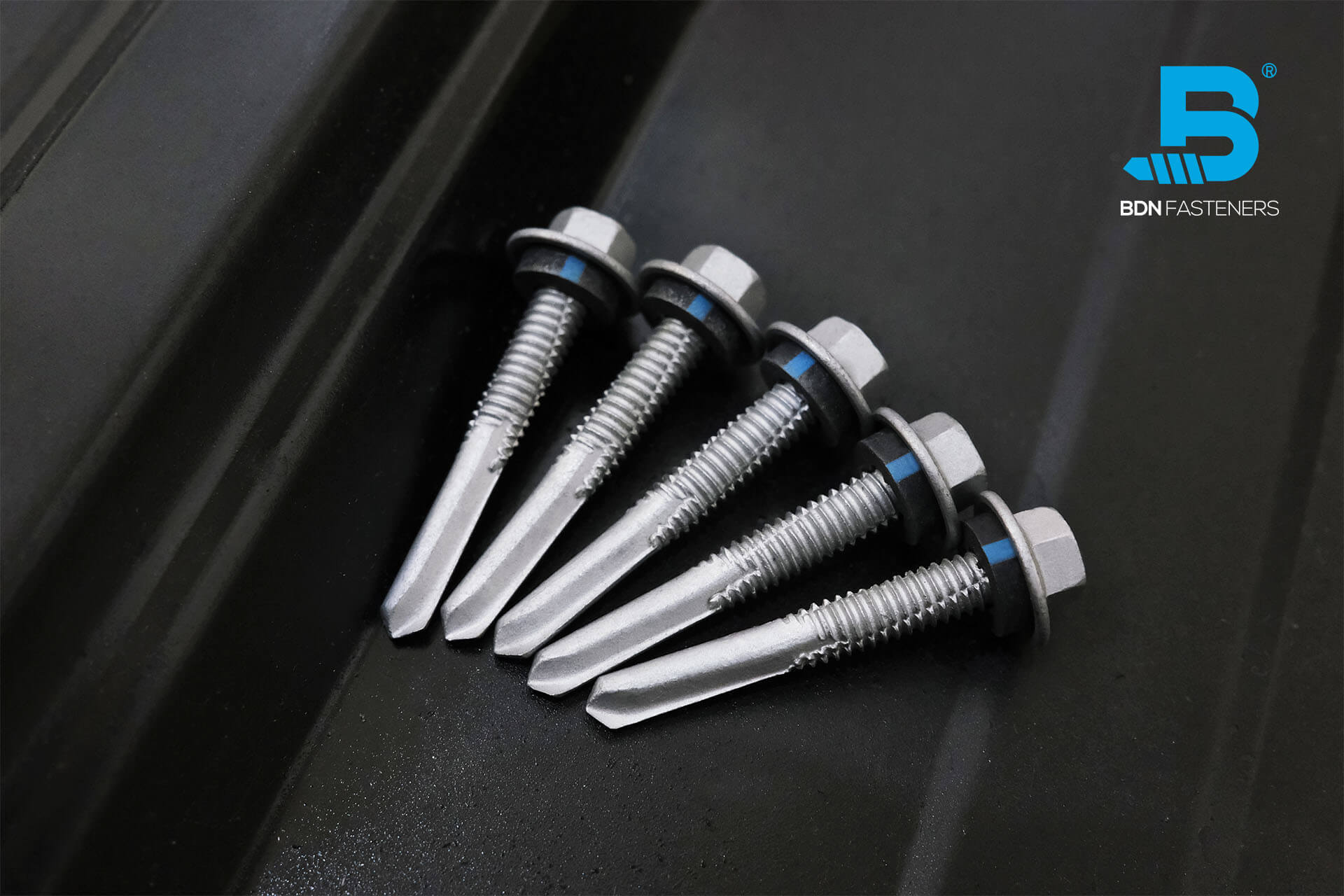
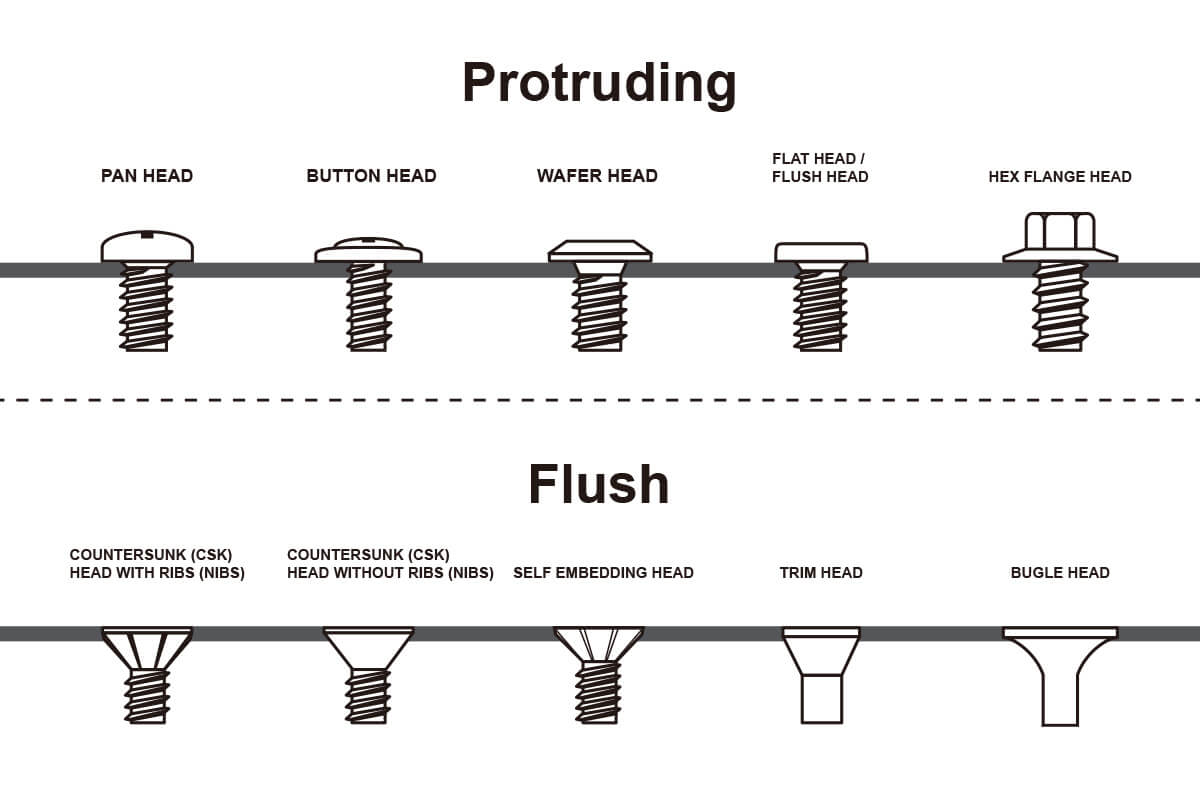
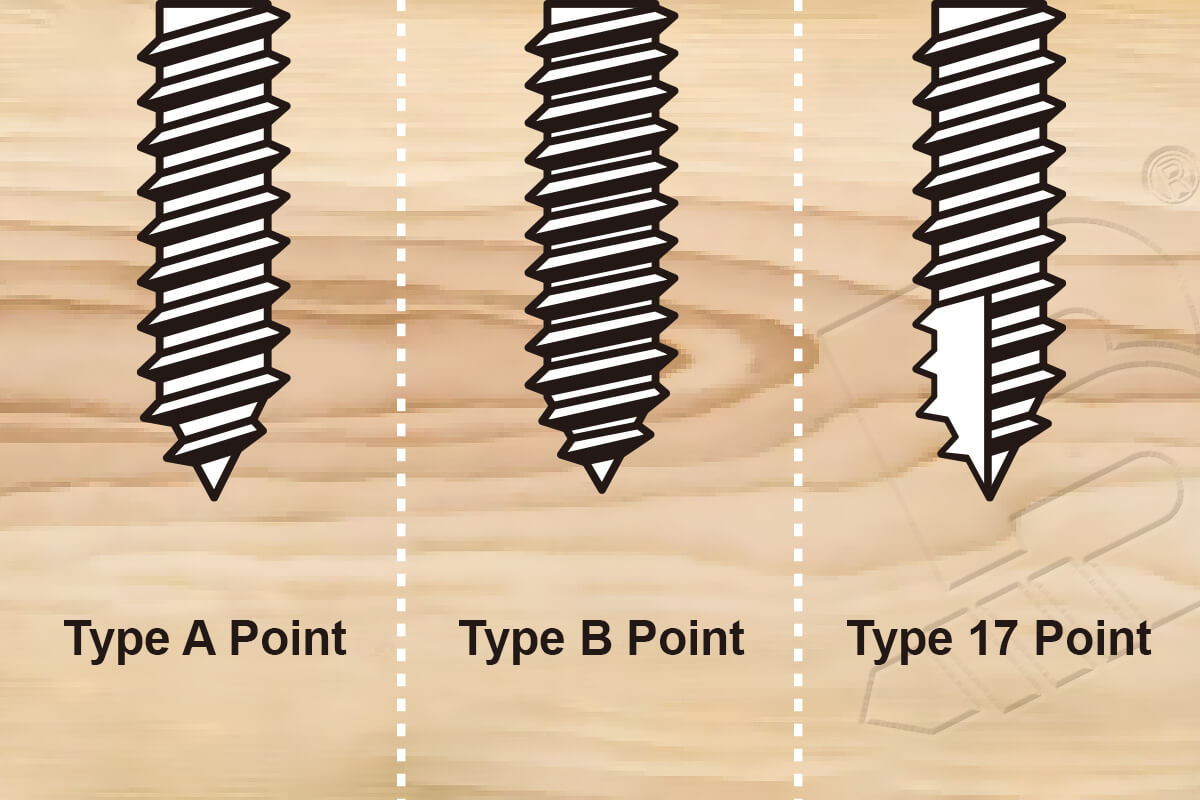
This is a question often brought up by DIYers, usually when trying to fix a broken piece of furniture, rebuilding part of a decking platform, or simply rejoining two pieces of wood that have somehow come loose with time – an age-old debate that started from before our time and continues until this day.
Both methods have proved its worth having survived for centuries, though none more so than the other, and we believe that it is down to choosing the best method to suit your needs.
When done manually, the difference in speed and precision between nails and screws installation was quite obvious. Nails were easier and faster to drive but had less precision, and screws offered pinpoint precision but was slow and laborious. However, the advancement of pneumatic and electric power tools for nail guns and screw guns have rendered the comparison pointless, as the tools made installation a breeze.
If speed and precision is out of the equation, one might wonder what else is left to compare? As a fastener manufacturer selling under our own brand name, it is imperative we provide accurate information to our customers. The choice between nails and screws of the same caliber all comes down the Shear strength, Tensile Strength, and Holding Strength.
- Shear Strength: The shear load required to break the screw, the ability to resist the pressure of two joined pieces “sliding” past each other.
- Tensile Strength: The tensile load required to break the screw, the ability to resist being pulled part, breaking under pressure.
- Holding Strength: How well the jointed substrates hold up against each other.
Nails tend to have better shear strength compared to screws, which means more flexibility, a very important feature suited for structural joining, framing, exterior wall sheathing, or hardwood floor installation. Nails made with correct materials will bend to a large angle and less likely to snap compared with screws.
Screws are better for delicate jobs and because the installation process involves less vibration, does not mar the surface, are easy to remove, and can be installed with precision. The tapping process during installation creates a tighter bond when reusing the original nail hole.
To summarize, use nails when joined surfaces are more likely to slide, and use screws for joined area which are more likely to pull apart, and on holes that previously had nails in them.